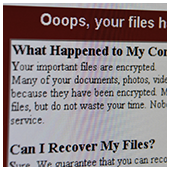
 The cyber community hasn’t fully recovered from the WannaCry ransomware attacks, which struck businesses and organizations in May. Now, a Petya ransomware variant named Nyetya is poised to join its ranks as one of the worst cyber attacks in history. Like WannaCry, its attackers exploited unpatched Microsoft vulnerabilities and demanded a $300 ransom in Bitcoins. But there are key differences between the two that are worth taking a look.
The cyber community hasn’t fully recovered from the WannaCry ransomware attacks, which struck businesses and organizations in May. Now, a Petya ransomware variant named Nyetya is poised to join its ranks as one of the worst cyber attacks in history. Like WannaCry, its attackers exploited unpatched Microsoft vulnerabilities and demanded a $300 ransom in Bitcoins. But there are key differences between the two that are worth taking a look.
Worse than WannaCry
Nyetya is deemed worse than WannaCry mainly because it spreads laterally, meaning it targets computers within networks and affects even systems that have been patched. Because it also spreads internally, it needs to infect only one device to affect several others within a single network.
Cyber researchers trace its origins to a tax accounting software called MEDoc, which infected 12,500 systems in Ukraine. Since the initial infections in June, it has spread to thousands of networks in 64 countries. And although it hasn’t spread as fast as WannaCry, it might have a wider reach soon because it uses three attack pathways to infect a system. It hasn’t made as much money as WannaCry, which is why cyber researchers are concluding that the attacks are not economically motivated.
Don’t pay the ransom
Cyber security firms and researchers strongly recommend affected businesses to avoid paying the ransom. According to them, paying the ransom would be a waste since the infected user won’t be able to receive a decryption key to unlock their files or systems. This is because the email provider has blocked the email address on the ransomware message.
Although it operates like a ransomware — locking hard drives and files and demands a $300 ransom in Bitcoin — it functions more as a wiperware that aims to permanently wipe out data and/or destroy systems. So far, it has affected big-name multinationals in various industries, including Merck, Mondelez International, and AP Moller-Maersk, among others.
Perform backups and update outdated security patches
The only way businesses can be protected is by performing backups and staying on top of patch updates.
It’s safe to say that in case of a Nyetya attack, there’s no chance of getting back your data. In such a scenario, you would have only your backup files — whether on an external storage or in the cloud — to fall back on. But backing up is not enough; you should also ensure that your backups are working, which you can do by testing them regularly. Given the nature of Nyetya, you should also make sure that your backups are stored off-site and disconnected from your network.
Like its predecessor, Nyetya exploited vulnerabilities in unpatched Microsoft-run computers. As a business owner, make it a part of your cyber security routine to update your systems with the latest security patches, or risk having your files or systems permanently corrupted.
As a business owner whose operations’ lifeline depends on critical files, your backups are your insurance. If your systems’ network security needs another layer of protection, get in touch with us today.

 Adding to the list of reasons to outsource your network security to a certified IT provider, a recent CIA leak shows just how vulnerable most network routers really are. Read on to learn why this is such a big vulnerability and what you can do to fix it.
Adding to the list of reasons to outsource your network security to a certified IT provider, a recent CIA leak shows just how vulnerable most network routers really are. Read on to learn why this is such a big vulnerability and what you can do to fix it. Security professionals should be beefing up your network security, implementing advanced firewall software, and identifying risks for possible breaches. In reality, they spend a huge chunk of their time troubleshooting issues on individual personal computers (PCs). That workflow is not ideal, but that’s what normally happens in many organizations. At what cost? Read on to find out.
Security professionals should be beefing up your network security, implementing advanced firewall software, and identifying risks for possible breaches. In reality, they spend a huge chunk of their time troubleshooting issues on individual personal computers (PCs). That workflow is not ideal, but that’s what normally happens in many organizations. At what cost? Read on to find out. WannaCry is one of the few malware campaigns to become a household name. It’s educated countless people on the reality of ransomware and the vulnerability of their data. If you’re still worried about whether you’re at risk, we’ve collected everything you need to know right here.
WannaCry is one of the few malware campaigns to become a household name. It’s educated countless people on the reality of ransomware and the vulnerability of their data. If you’re still worried about whether you’re at risk, we’ve collected everything you need to know right here. The WannaCry ransomware, a type of malware that encrypts a victim’s files and extorts them for money, has already affected thousands of machines worldwide. Unfortunately, the success of this attack is just the beginning. According to security researchers, other hackers will probably develop stronger WannaCry variants in the coming months. And if you don’t want your business to become a victim of these attacks, you must take the following precautions.
The WannaCry ransomware, a type of malware that encrypts a victim’s files and extorts them for money, has already affected thousands of machines worldwide. Unfortunately, the success of this attack is just the beginning. According to security researchers, other hackers will probably develop stronger WannaCry variants in the coming months. And if you don’t want your business to become a victim of these attacks, you must take the following precautions.